Digital asset storage has always been a trouble for institutions with millions and billions of dollars in holding. The complicated dynamics of keeping assets secure and agile still creates a barrier for greater institutional adoption.
This is particularly true of the stigma around ‘wallets’ and how different the process of storing digital assets in these wallets is from the traditional methods of using bank accounts.
Digital asset wallets are notorious for their inefficiencies, from single points of failure to not being fully chain agnostic, from a subpar transactional experience to easy asset transfer across different wallets.
Unlock the potential of digital assets for your institution
To break through the difficulties in securing assets on a single person signatory self-custodial wallet, technologies like MPC and Multi-Sig were designed by wallet engineers to add the power of decentralization into wallets and making it possible to overcome the basic bottlenecks in single-sig wallets. These wallets facilitates institutions with an efficient way to secure their assets, manage private key and move assets in a streamlined manner.
If you are dealing with digital assets natively or hold in your investment portfolio as an organization, figuring out what wallet type to use can be significant decision leading to the foundation of your security infrastructure. Let me help you figure out which type; Multi-Sig or MPC wallet is the right option for you business needs.
What makes MPC and Multi-Sig wallets functional?
Multisig and MPC wallets are better alternatives and address some of the significant design flaws that single-signature wallets possess. These MPC and multisig wallets require multiple users to approve, verify, and sign all types of transactions.
Secure and manage your digital assets with Liminal
In the light of how vulnerable institutions wallets are, adding the layer of multiple signer, assing the access to right stakeholders and sharding private key becomes inevitable to achieve full control and safeguard wallets explicitly.
Private Key – Public Key Infrastructure
Private Key – Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) is a fundamental concept in cryptography and digital security.
In this infrastructure, each user or entity has a pair of cryptographic keys: a private key and a public key. The private key is kept secret and known only to the owner, while the public key can be freely distributed.
These keys are mathematically related, with data encrypted by the public key only able to be decrypted by the corresponding private key, and vice versa.
PKI facilitates secure communication and authentication in various digital processes, including secure email communication, digital signatures, and SSL/TLS certificates for website encryption.
In the case of digital asset wallets, private key is responsible for signing all transactions initiated from your wallet. In hindsight, the private key represents absolute ownership of all on-chain assets. Safeguarding private keys, without a doubt, is the most important factor for any institution when dealing with digital assets on a massive scale.
On the other hand, the public key is utilized to identify and send cryptocurrency into a wallet.
Multi-Signature Wallets
Multi-signature wallets are cryptocurrency wallets that require multiple or more than one signature to verify ownership and execute transactions. During the multisig wallet setup process, the transaction signing authority is assigned to the respective members of your trusted group.
The fund owner can specify the minimum number of signatures required to execute any type of official transaction. Multisig wallets allow you to set a minimum signature threshold that can be lower than the total number of participants in the group. Every participant in the group will be assigned one private key. Every person in the group has the authority to partially sign the transaction until the requisite number of signatures is fulfilled.
To prevent a single key owner from unilaterally transferring funds, the multi-signature wallet allows groups to set up in any “m” out of the “n” combination, where “m” is the number of signatures required to execute transactions; on the other hand, “n” signifies the number of private keys users hold within the trusted group. This setup and execution process helps verify ownership and ensure the legitimacy of the transactions.
Multi-Party Computation (MPC) Wallets
Multi-part computation wallets or MPC wallets is, a cryptographic tool that employs cryptographic data from multiple parties owning multiple devices to perform calculations using their combined data points without revealing their individual input.
The MPC wallet doesn’t use multiple private keys like a multisig wallet; it splits and distributes a single private key into multiple smaller parts using algorithms. In other words, the MPC wallet distributes the signature process across multiple computing devices. Later, these algorithmically distributed keys are processed to generate a whole private key. Once the private keys are generated, the MPC wallet can conduct a verified transaction with the help of a digital signature created by the shared private key.
Additionally, the MPC wallet allows digital asset owners to sign transactions while keeping the shared key private – this is critical for ensuring fund security in the long run. The fact that MPC provides a comprehensive constitution of operational flow into a conceptually secured framework, makes it a go-to choice for bigger institutions.
Similarities Between MPC & Multi-Sig
Distributed Control: Both MPC and multi-sig wallets offer controlled distribution of wallet access to multiple parties or entities. This level of decentralization configured into institutional wallets, where transactional decisions needs to be taken in a group bodes well. This approach by both wallet types inherently reducing the risk of fraud or unauthorized access.
Resilience to Compromise: Both MPC and Multi-Sig wallets are designed to withstand compromises of individual participants or components. Recovery of assets as a concept was not common, before these two wallet technologie made it possible in their own sense. The fac t that even if some parties or keys are compromised, the overall security of the system remains intact as long as a sufficient number of participants or signatures are still valid, is proof enough that currently most institutions are looking to switch their wallet types to either the one.
Flexibility: Both MPC and multi-sig can be customized and configured to meet specific security requirements and use cases. They provide flexibility in choosing the number of participants or signatures required for a transaction, as well as the types of cryptographic algorithms and protocols used.
Trust Minimization: Both MPC and Multi-Sig techniques aim to minimize the level of trust required among participants. By distributing control and using cryptographic protocols, MPC and multi-sig enable parties to interact and transact with each other without fully trusting one another.
Key Difference Between MPC Wallets and Multi-sig Wallets
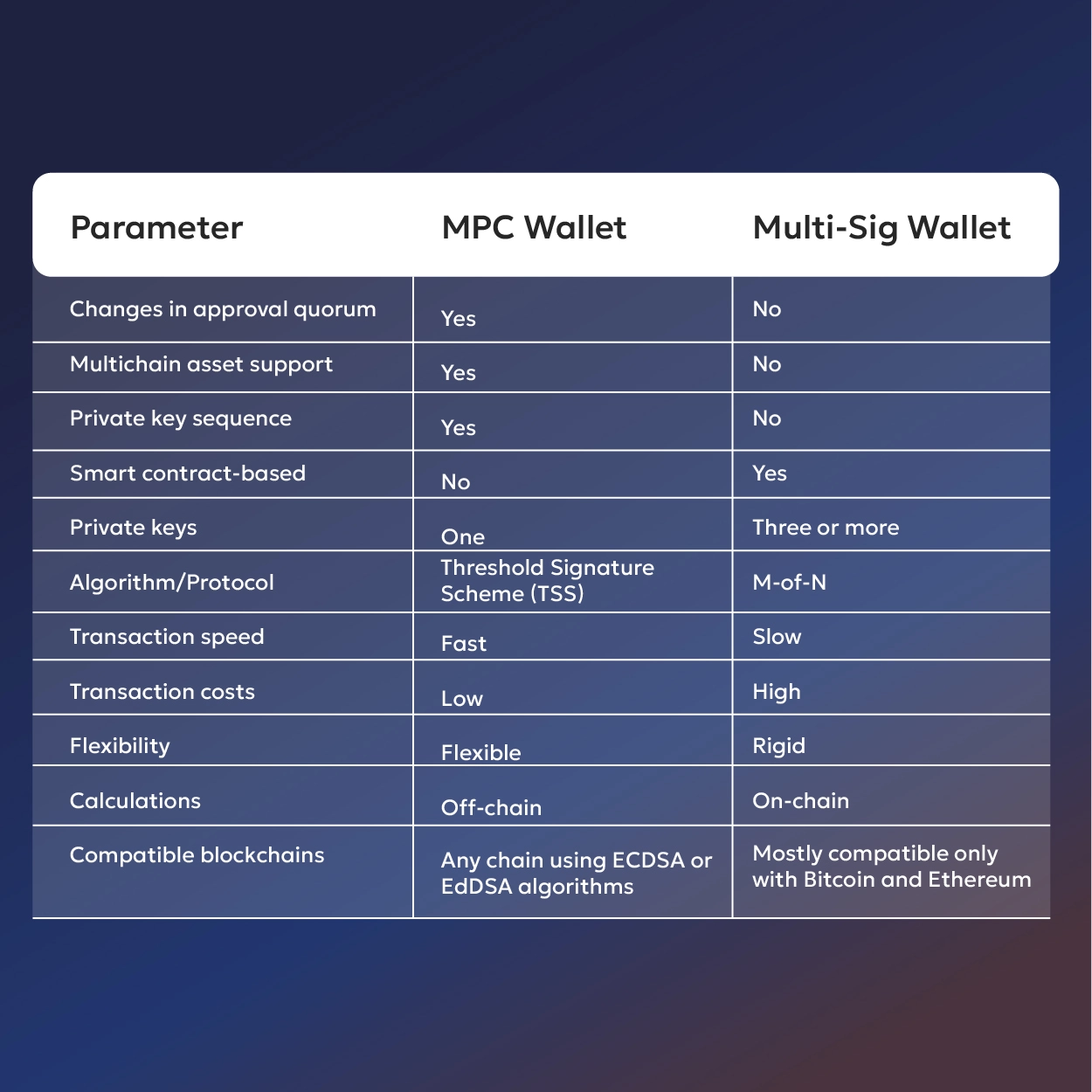
Which Wallet Is Ideal For Institutions? MPC or Multi-Sig
Amongst all the chatter around digital asset wallets being extremely vulnerable and increasing number of hacks institutions are facing due to internal or external factors, onset of MPC and Multi-Sig have changed the game for institutions, fastening their wallet security to new levels.
Now, both of these wallets we discussed above makes sense to deploy basis how a particular institutions approaches custody of their assets, easy of convininance, assets under management, stakeholders involved in the process of signing and integration capabilities.
MPC makes sense for institutions like Exchanges, Hedge Funds, VCs and Market Makers, Family Offices. Multi-Sig makes sense for institutions like Web3 protocols, Treasuries & DAOs and Government Bodies.
Remember, this guide serves as a starting point, and further research is crucial before making any financial decisions.







